How To Bleed Kelsey Hayes Abs Module

Abode, Auto Repair Library, Automobile Parts, Accessories, Tools, Manuals & Books, Car Weblog, Links, Alphabetize
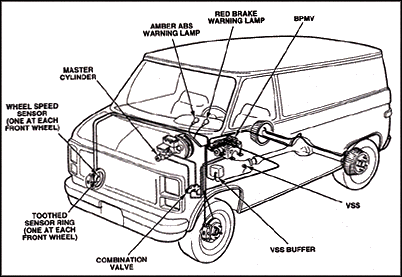
Kelsey-Hayes 4WAL Antilock Brakes
Copyright AA1Car.com
In 1990, Kelsey-Hayes introduced a new four-cycle anti-lock braking organisation (EBC4) on General Motors M- and L-series minivans (Chevrolet Astro and GMC Safari). General Motors refers to the system as 4WAL. The following year 4WAL was offered on the S- and T-series trucks (Chevy Blazer, GMC Jimmy iv-door) and the GMC Syclone. In 1992, the four-bike anti-lock braking organisation was added to the two-door S- and T-series trucks, Suburban, total-size Blazer/GMC Yukon, Geo Tracker and the express-product GMC Typhoon.
The 4WAL organisation is a nonintegral, iv-wheel, three-channel ABS system with a conventional master cylinder and brake booster. Each forepart restriction circuit is controlled independently, but both rear brakes are controlled as a pair. The system also functions in 4-wheel drive, so information technology is a fulltime system different some of the earlier RWAL Rear Wheel Antilock Brake applications where the ABS system was deactivated when switching from two- to four-bike drive.
On most 4WAL applications, 4 cycle speed sensors are used (one for each wheel). On the 1992 Suburban, however, merely the front wheels have individual speed sensors. A transmission-mounted vehicle speed sensor provides a common signal for both rear wheels.
The front bicycle speed sensors on two-wheel-drive trucks are located on the splash shield behind the brake rotor, with the sensor ring behind the rotor. On four-wheel-drive trucks, the front sensors are mounted behind the splash shield and can be replaced without having to pull the restriction rotor. The tone band, however, is part of the wheel bearing assembly. Air gaps on both types of front cycle speed sensors are nonadjustable and are factory prepare at .050 inches.
The rear cycle speed sensors are located on the rear restriction bankroll plates with rings pressed onto the ends of the beam shafts. The air gap is nonadjustable.
On all 4WAL applications except the 1992 Suburban, the signals from the wheel speed sensors go straight to the electronic control unit (no DRAC module is used). Only on the Suburban, the speed sensor point for the rear wheels commencement goes through an electronic "buffer" that's like to the DRAC module in RWAL applications. The buffer divides up the vehicle speed signal into various frequencies that are used by the cruise-command organisation, engine-command module and electronic speedometer and odometer, as well every bit the anti-lock brake system.
The ABS command module is mounted on the hydraulic modulator assembly, which General Motors calls the Electro-Hydraulic Command Unit of measurement (EHCU). I variation is the EBC4-VCM system on 1994 and up Chevy Due south- and T-series trucks. On these applications, at that place is no ABS control module on the modulator. The ABS control electronics have been integrated into the engine command module then a single module controls both systems.
The ABS control module receives input from the wheel speed sensors and a brake pedal switch. On trucks with automatic transmissions, the brake switch circuit contacts besides command power to the transmission torque converter clutch. The switch is normally airtight, and provides a 12-volt electrical betoken to the ABS controller. With the brake pedal practical, the switch opens and supplies less than one volt to the controller.
The 4WAL organisation too has a 4WD switch and indicator lite. The 4WD switch is needed to change the ABS control logic when the vehicle is shifted into four-wheel drive. The switch is mounted on the forepart axle in T-series trucks, and is open up in ii-bike drive, supplying less than one volt to the controller. The switch is closed in four-cycle bulldoze and supplies 12 volts to the controller. The switch is role of the indicator lite circuit and is mechanically operated by the shift linkage in the transfer case.

For diagnostic purposes, there'south both a red Restriction and bister ANTI-LOCK alert light - instead of the unmarried red BRAKE warning light that'southward used on Kelsey-Hayes rear-bicycle ABS systems. There is also an Assembly Line Diagnostic Link (ALDL) diagnostic connector which can be used for manual mistake code retrieval or diagnosing with a browse tool.
KELSEY-HAYES 4WAL ELECTRO-HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT (EHCU)
The EHCU contains six ABS solenoid valves, an isolation valve and a modulation valve for each of the 3 private brake circuits. The EHCU too has a single pump motor that drives ii separate pumps (1 for the front brakes and the other for the rear brakes). The relay for the pump motor is located inside the EHCU. Also inside the EHCU are iv pressure accumulators - ane front and one rear low-pressure accumulator, and one front and one rear high-force per unit area accumulator. There are likewise 3 reset switches (ane for each front brake and one for the combined rear brake excursion). The EHCU is located nether the master cylinder in the engine compartment on the Astro and Safari vans, and on the left wheel well on S- and T-series Blazers.
KELSEY-HAYES 4WAL SYSTEM Performance
During normal braking, fluid pressure level from the main cylinder passes through the normally open isolation and modulation solenoid valves in the EHCU to the private brakes. But, when the controller senses that bike lockup is most to occur during braking, it activates anti-lock braking.
The EHCU begins ABS operation in the usual way by energizing the ABS isolation solenoid for the affected wheel to block any further force per unit area increase to the restriction. At the same time, the pump motor relay is energized to get-go the pump. This primes the system and builds pressure in the high-pressure accumulator for the force per unit area increment phase of anti-lock braking. The side by side footstep is to energize the delay ABS solenoid, which is referred to as the Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM) valve, to drain pressure from the brake. The 4WAL control module can vary the amount of force per unit area subtract by varying the valve'due south open or ON time. It does this by varying the ON time or elapsing of the voltage to the solenoid.
When the PWM valve is energized and closes, it opens a passage that allows pressure to be released from the brake circuit. The pressure is dumped into one of the two depression-force per unit area accumulators. The jump-loaded depression-pressure accumulator (LPA) serves equally a temporary storage reservoir to hold the fluid until information technology can be rerouted dorsum into the system. It likewise maintains sufficient fluid pressure in the EHCU to continue the loftier-pressure pump primed.
Equally force per unit area is reduced in the brake circuit that's being controlled, the reset switch for that circuit may trip signaling the ABS command module that fluid pressure has dropped to the point where boosted force per unit area is needed to maintain proper braking activity. At this point, the command module will de-energize the PWM valve and initiate the pressure increase manner.
When the PWM reopens, fluid pressure from the high-pressure accumulator (HPA) and loftier-pressure level pump enters the restriction excursion and builds brake pressure level. This reapplies the brake equally the wheel continues to decelerate. This reset switch too returns to its normal position as pressure is restored. The ABS controller then continues to cycle the PWM valve as needed to forestall wheel lockup for the duration of the stop.
During the pressure level concord, decrease and increase phases of anti-lock braking, the isolation valve for the brake circuit remains closed. This blocks brake pressure from the master cylinder so it tin't enter the restriction circuit existence controlled. The reapplication of brake pressure, therefore, must come from the loftier-pressure pump and accumulator.
Once the need for ABS braking has passed, the isolation and PWM valves are de-energized and normal braking is restored. The residual force per unit area that remains in the high-pressure accumulator is bled off into the master cylinder reservoir and the arrangement returns to the passive mode until information technology is needed again.
KELSEY-HAYES 4WAL ANTILOCK Restriction DIAGNOSTICS
The self-diagnostic capabilities of the 4WAL system are much ameliorate than the earlier RWAL or RABS organisation, and include more than mistake codes and the ability to log and brandish multiple codes. The controller monitors all system inputs while driving, and performs an automated cocky-examination every time the vehicle is started and driven faster than eight mph. Initial cocky-checks tin reveal problems such equally opens or shorts in the wheel speed sensors, internal issues in the electronic controller, and issues in the ABS and brake light warning circuits.The cocky-diagnostics will as well check for aberrant bike speed sensor readings at speeds above three mph. When the vehicle reaches viii mph, the controller cycles the solenoids, relays and pump motor to cheque their performance. The auto test may be heard and felt by the driver while it is taking place, but does non indicate a problem. If the restriction pedal is depressed (or the switch is open), the system volition not perform the cocky-test until the pedal is released.
The controller will illuminate the amber ABS alert light when a error is detected, log a code and disable the ABS system. The ABS light volition remain on equally long every bit the key is on, and volition come on again the next time the engine is started if the trouble however exists. If the trouble is intermittent, the warning low-cal volition not come back on until the problem repeats unless it is a "difficult" (latching) lawmaking. A difficult code will keep the ABS alarm calorie-free on until the code is cleared from memory.

If a fault occurs in the ABS alarm-light circuit, the red brake alert light volition come on to alert the driver to ABS issues. The brake alert light will also come on if there is a hydraulic failure in either restriction circuit.
KELSEY-HAYES 4WAL Organization PRECHECKS
Prior to checking the organisation for mistake codes, the vehicle should be given a preliminary visual inspection to check for obvious problems:- Confirm whether or not the amber ABS and/or carmine restriction warning lamps are all the same on by doing a bulb check and then starting the engine. If the lamp remains on, the system has an ABS fault lawmaking and requires farther diagnosis.
If the lamp goes out, either no faults have been detected, or the fault is intermittent or a soft (non-latching) fault. - If the brake and ABS warning lamps fail to illuminate when the key is turned on, check all system fuses including the ones for the musical instrument cluster.
- Check the brake warning low-cal by turning the key on and applying the parking brake. The light should come on. It should then go out when the brake is released.
- Check the wiring harness connectors on the modulator.
- Check the level of the brake fluid.
KELSEY-HAYES 4WAL ANTILOCK BRAKE TROUBLE CODES
The 4WAL system provides manual flash codes, and tin as well be accessed with a browse tool. Here's the manual procedure.one. Connect a jumper wire betwixt pin "A" and pin "H" on the diagnostic connector under the musical instrument panel (or ground pin "H"), and plow the ignition on. This puts the organisation into the cocky-diagnostic manner.
ii. Codes are displayed by flashes of the ABS alarm light. Count the flashes to make up one's mind the lawmaking number. If the ABS warning light circuit is defective, the codes will exist flashed out by the brake warning light.
The first series of flashes will represent the first digit of the fault code. The 2d serial of short flashes that follow a brief break represent the second digit of the code. A code 12, for example, would appear as a flash, pause, flash, wink.
One of the codes received will be a normal system code: lawmaking 12 with the brake non applied in the 2WD style; code xiii with restriction applied in 2WD fashion; code 14 with restriction not applied in 4WD mode; or code xv with brake practical in 4WD mode. This normal code allows the brake and 4WD switches to be tested without having to utilize a browse tool.
Each lawmaking will repeat three times earlier the next lawmaking is displayed.
To erase stored fault codes, a scan tool or the post-obit manual procedure can be used.
one. Plough the ignition switch on.
2. Connect a jumper wire or key betwixt diagnostic connector terminals "H" and "A" (or ground "H") - and wait two seconds.
iii. Remove the jumper wire for ane second.
iv. Repeat the grounding for ii more than seconds. The ABS warning light should go out if the codes have been successfully erased.
This process is necessary only on sure hard codes. Soft codes tin can be cleared by correcting the system problem and turning the ignition off for approximately 5 seconds.
KELSAY-HAYES 4WAL SCAN TOOL DIAGNOSIS
The Kelsey-Hayes 4WAL ABS organisation can too exist diagnosed with a scan tool. However, a bi-directional scan tool with the appropriate software is necessary to read history codes and to perform various tests. These include:- Check voltages at the diagnostic connector terminal "H."
- Bike speed sensor output (in miles-per-hour) from each sensor.
- Reset switch status (right forepart, left front and rear).
- Function tests of the hydraulic modulator.
- Capture "snapshot" data during a test bulldoze for afterward analysis.
History codes in the 4WAL system reveal the number of ignition drive cycles since a fault occurred. A drive bike is defined equally the vehicle existence started and driven above a specified speed, usually nigh eight mph with the 4WAL organization.
KELSAY-HAYES RWAL LOW PEDAL PROBLEM
A pedal that gradually sinks to the floor usually indicates a worn master cylinder. But on Kelsey-Hayes rear-bicycle ABS applications, the condition may exist caused by dirt in the ABS modulator valve. Dirt can prevent the dump valve from fully seating and let rear brake pressure level to leak past the valve.
To isolate the trouble, disconnect the steel brake line from the master cylinder that supplies the rear brakes. So accept a helper depress the restriction pedal about an inch to purge air from the outlet port. Install a tube plug in the port and tighten it, making sure pedal pressure is maintained to forbid harm to the primary cup every bit it moves across the vent port in the master cylinder. If the pedal continues to sink after the plug is installed, the master cylinder is leaking and needs to be replaced. If the pedal holds firm, even so, so the problem is in either rear restriction circuit or the ABS command valve. To pinpoint the problem, cake off the outlet port at the ABS command valve and recheck pedal feel every bit before. If the pedal now feels hard, the problem is probably a leaky rear cycle cylinder. Just if the pedal continues to sink, the ABS dump valve is leaking and the ABS control valve associates needs to be replaced.
KELSEY-HAYES 4WAL Bleeding Process
Brakes can be bled in the usual way manually or with pressure or vacuum equipment. The cycle bleeding sequence is RR, LR, RF, LF. If a pressure bleeder is used, the combination valve must be held open.
If the EHCU Modulator or accumulator have been replaced, or air has entered the ABS part of the organization, the EHCU modulator volition take to be bled using one of two special procedures:
The preferred method is to cycle the ABS system using a mill scan tool or an aftermarket pro-level scan tool that has bi-directional capabilities so it tin can admission the ABS system and cycle the pump and solenoids. A basic DIY scan tool that merely reads codes and sensor data cannot do this.
If you can't go your hands on the proper scan tool, you can use the following manual bleeding process:
1. First, bleed the entire brake system using a force per unit area bleeder or vacuum bleeder. Pumping the brake pedal besides works only must exist done advisedly so air doesn't siphon back into the lines. Bleed the wheels in this order: Right Rear, Left Rear, Right Front, Left Front end.
2. In one case all the air is out of the main cylinder and brake lines (no bubbles in the clear plastic bleeder hose you lot have fastened to each of the calipers or wheel cylinders), you tin proceed to bleeding the ABS system.
3. Open the internal bleed screws on the modulator one quarter to a one-half-turn. These are the cap screws on either side of the modulator. Note: Some newer 4WAL systems do NOT have these bleed screws then you lot must use a scan tool to bleed the system or try loosening the brake lines to the modulator to vent air.
4. Connect special tools (such equally Kent-Moore No. J39177) to agree open the high-pressure accumulator bleed valves.
5. Open the two bleeder screws at the BPMV and bleed the unit of measurement by forcing fluid through it with a pressure bleeder or by slowly pumping the brake pedal. Do Non allow the master cylinder reservoir to run low (add together brake fluid as needed during this procedure).
6. Drain the wheels once again as before: RR, LR, RF, LF
7. Tighten the modulator bleed screws and remove the tools from the loftier-pressure accumulators.
eight. Plough the ignition on and start the engine. Printing down firmly on the restriction pedal several times. If the pedal does not experience house, plough the engine off, pump the pedal to relieve residual pressure in the system, and bleed each of the iv brakes as before to get rid of any air in the arrangement.
It's a pain to go through all of these steps, but if you lot do not and air is trapped in the ABS unit (or pump on applications that have a pump), it volition eventually go into the lines and give yous a soft pedal.
 Related Antilock Brake Manufactures
Related Antilock Brake Manufactures
Antilock Brake SystemsABS System Application Chart (by vehicle year, brand & model)
Antilock Braking Systems (1998 model yr)
ABS Systems Come Under Fire
New ABS Diagnostic Testers
Pulling ABS Diagnostic Codes
Diagnosing ABS Wheel Speed Sensors
Honda Antilock Brakes
Chrysler Dodge Plymouth Minivan Bendix x Antilock Brakes
GM Delphi DBC-7 ABS Antilock Brakes
Jeep Bendix 9 Antilock Brakes
Kelsey-Hayes RWAL Rear Wheel Antilock Brakes
Teves Marker 20 Antilock Brakes
Electronic Stability Control
Restriction-By-Wire
Antilock Brake Guide product information
GM SUV Recall for ABS problem (August 2005)
Fixes For Common Restriction Problems
 Click Here to See More Carley Automotive Technical Articles
Click Here to See More Carley Automotive Technical Articles

Click Here for Quick Reference Guide to Antilock Brakes

Click Here for Brake Repair Guide
Be sure to visit our other websites:

Car Repair Yourself
Carley Automotive Software
OBD2HELP
Random-Misfire
ScanToolHelp
TROUBLE-CODES
Source: https://www.aa1car.com/library/abs_kelseyhayes.htm

0 Response to "How To Bleed Kelsey Hayes Abs Module"
Post a Comment